Combined Heat and Power facilities, also called cogeneration or
co-gen plants, lower costs and reduce CO2 emissions by
producing both heat and electricity from a single heat source -
waste heat from thermal power plants. They capture the waste
heat from conventional power plants and re-use it, thereby reducing
the amount of fuel needed to produce the same amount of useful
energy. This efficiency gain results in lower fuel costs and
lower CO2 emissions.
Significant Market Potential - The DOE has set an aggressive
goal to have CHP comprise 20% of power generation by 2030 with
current capacity at just 8%. The current energy lost from waste
heat in the United States is greater than the total energy usage of
Japan!
ACCORDING TO THE UNITED STATES CLEAN HEAT & POWER
ASSOCIATION, COMBINED-HEAT-AND-POWER SYSTEMS CURRENTLY PROVIDE THE
FOLLOWING ECONOMIC AND ENVIRONMENTAL VALUE:
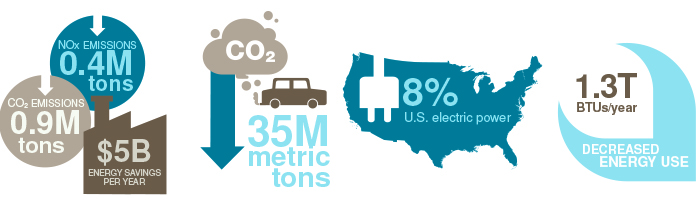
• Reduce NOx emissions by 0.4 million tons per year
• Decrease energy use by almost 1.3 trillion BTUs per
year
• Save building and industry owners more than $5 billion
per year in energy costs
• Prevent the release of over 35 million metric tons of
carbon equivalent into the atmosphere
• Produce almost 8 percent of U.S. electric power
• Reduce CO2 emissions by over 0.9 million tons per
year